Ap euro period 1 review – Embark on an extraordinary journey through AP Euro Period 1, a captivating era that laid the foundation for the modern world. From the Renaissance and Reformation to the Scientific Revolution and the Enlightenment, we delve into the pivotal events and ideas that shaped European society.
Uncover the political, economic, and social transformations that characterized this period. Explore the rise and fall of empires, the clash of ideologies, and the profound impact of scientific discoveries on human thought and society.
Historical Context of Europe
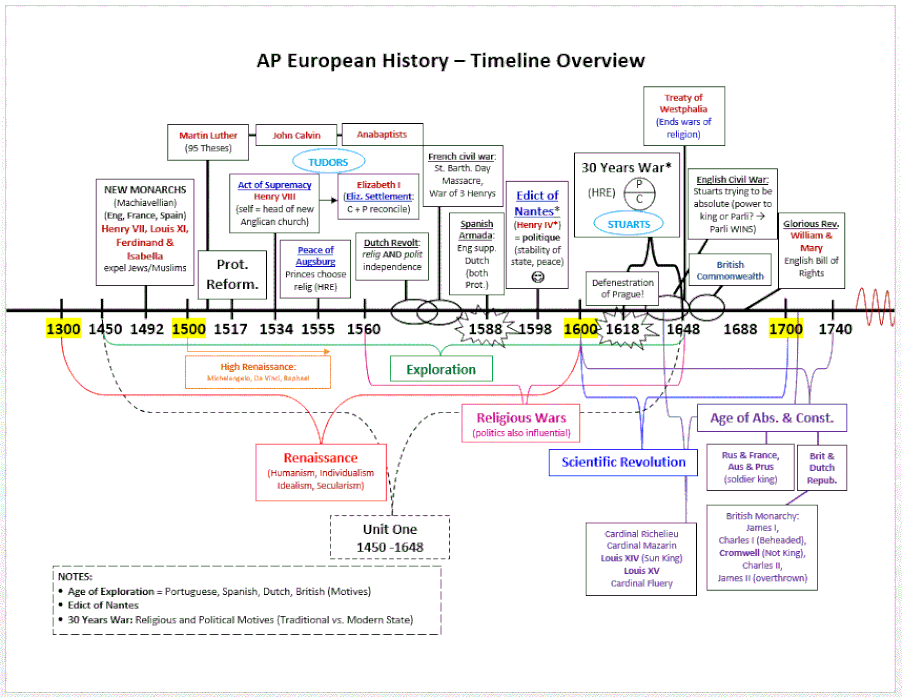
Period 1 of European history encompasses a period of significant political, economic, and social transformation. From the fall of the Roman Empire to the rise of the Renaissance, Europe underwent profound changes that shaped its cultural, political, and economic landscape.
Political Developments, Ap euro period 1 review
- Feudalism: A decentralized political system based on landownership and military service.
- Manorialism: A system of economic organization centered around large estates.
- Crusades: Religious wars fought by European Christians to regain control of the Holy Land.
Economic Developments
- Agricultural Revolution: Technological advancements that increased agricultural productivity.
- Trade and Commerce: The growth of trade and the emergence of towns and cities.
li> Guilds: Associations of merchants and artisans that regulated trade and crafts.
Social Developments
- Christianity: The dominant religion in Europe, shaping social and political life.
- Monasticism: The practice of religious life in monasteries and convents.
- Chivalry: A code of conduct for knights and nobles, emphasizing honor and loyalty.
Renaissance and Reformation

The Renaissance and Reformation were two major cultural and religious movements that transformed Europe during the 15th and 16th centuries. The Renaissance, which originated in Italy, emphasized humanism, scientific inquiry, and artistic innovation, while the Reformation, a religious movement that began in Germany, challenged the authority of the Catholic Church and led to the establishment of Protestantism.
Origins and Characteristics of the Renaissance
The Renaissance was a period of renewed interest in classical learning and culture. Humanism, a philosophical movement that emphasized the importance of human reason and experience, became central to Renaissance thought. Renaissance scholars studied ancient Greek and Roman texts, leading to advances in literature, philosophy, and science.
Artistic Innovation during the Renaissance
The Renaissance also witnessed a flowering of artistic innovation. Artists such as Leonardo da Vinci, Michelangelo, and Raphael created masterpieces that combined classical forms with new techniques and perspectives. Renaissance art emphasized realism, emotion, and the beauty of the human body.
Origins and Characteristics of the Reformation
The Reformation began with the posting of Martin Luther’s Ninety-Five Theses in 1517. Luther criticized the Catholic Church’s practices, including the sale of indulgences and the authority of the pope. His ideas quickly spread throughout Europe, leading to a widespread challenge to the Catholic Church.
Religious Conflicts and Political Upheaval
The Reformation sparked religious conflicts and political upheaval throughout Europe. Protestants and Catholics fought in wars, and many Protestants were persecuted. The Reformation also led to the rise of new Protestant denominations, such as Lutheranism, Calvinism, and Anglicanism.
Exploration and Colonialism
Exploration and colonialism were major themes of Period 1 in European history. Driven by a thirst for wealth, power, and knowledge, European nations embarked on ambitious voyages of discovery that would profoundly impact the world.
As you delve into the intricacies of AP Euro Period 1, remember that supplemental practice can enhance your understanding. For a quick refresher, check out the Abeka Algebra 1 Quiz 28 . It offers concise summaries and targeted questions to reinforce your grasp of key concepts.
By incorporating this resource into your AP Euro Period 1 review, you’ll gain a deeper understanding of the era and its lasting impact.
Motivations and Methods of European Exploration
The motivations for European exploration were multifaceted. Economic factors, such as the desire for new trade routes and access to exotic goods, played a significant role. Political ambitions, including the quest for territory and imperial expansion, also fueled the drive to explore.
Additionally, intellectual curiosity and a thirst for knowledge about the wider world spurred many explorers onward.
European exploration methods evolved over time. Early voyages relied on rudimentary ships and navigational techniques. As technology improved, ships became larger and more seaworthy, and navigational instruments such as the compass and astrolabe became more accurate. This allowed explorers to venture further and more confidently into unknown waters.
Impact of European Colonialism
European colonialism had a profound impact on the Americas, Africa, and Asia. European powers established colonies in these regions, often exploiting their resources and subjugating their populations. This had devastating consequences for indigenous peoples, who were often displaced, enslaved, or killed.
However, European colonialism also had some positive effects. It introduced new technologies, crops, and ideas to the colonized regions. In some cases, it led to the development of new societies and economies. However, the overall legacy of European colonialism is complex and often negative.
Consequences of European Expansion
The economic, political, and cultural consequences of European expansion were far-reaching. Economically, it led to the growth of trade and the emergence of a global economy. Politically, it led to the rise of European empires and the establishment of a new world order.
Culturally, it led to the spread of European ideas and values around the world.
Scientific Revolution
The Scientific Revolution was a period of great intellectual and scientific upheaval in Europe that began in the 16th century and lasted until the 18th century. During this time, new scientific discoveries and theories emerged, which challenged the traditional Aristotelian view of the world and laid the foundation for modern science.
One of the most important scientific discoveries of this period was the heliocentric model of the solar system, which was proposed by Nicolaus Copernicus in the 16th century. This model placed the Sun at the center of the solar system, with the Earth and other planets revolving around it.
This theory was a radical departure from the traditional geocentric model, which placed the Earth at the center of the universe.
Another important scientific discovery of this period was the development of the scientific method, which was pioneered by Francis Bacon and René Descartes. The scientific method is a systematic approach to scientific inquiry that involves making observations, forming hypotheses, and testing those hypotheses through experimentation.
This method allowed scientists to test their ideas and theories in a rigorous and objective way.
The Scientific Revolution had a profound impact on European thought and society. It led to a new understanding of the natural world and the human place in it. It also led to the development of new technologies and inventions, which improved the quality of life for people all over the world.
The Scientific Revolution is often seen as the beginning of the modern world. The discoveries and theories that emerged during this period laid the foundation for the scientific and technological advances that have shaped our world today.
The Role of Scientific Inquiry in Shaping the Modern World
Scientific inquiry has played a vital role in shaping the modern world. It has led to the development of new technologies and inventions, which have improved the quality of life for people all over the world. It has also led to a new understanding of the natural world and the human place in it.
Some of the most important scientific discoveries and inventions that have shaped the modern world include:
- The development of the telescope, which allowed astronomers to observe the stars and planets in greater detail.
- The invention of the microscope, which allowed scientists to observe the microscopic world for the first time.
- The discovery of electricity, which led to the development of new technologies such as the electric light bulb and the electric motor.
- The development of the internal combustion engine, which led to the development of the automobile and the airplane.
- The discovery of penicillin, which led to the development of antibiotics and the treatment of bacterial infections.
These are just a few of the many scientific discoveries and inventions that have shaped the modern world. Scientific inquiry continues to play a vital role in our world today, and it is likely that it will continue to shape our world in the future.
Absolutism and Enlightenment
The 17th and 18th centuries witnessed a profound transformation in European political thought and society. The rise of absolutism, characterized by the concentration of power in the hands of monarchs, shaped political structures and social hierarchies. Simultaneously, the Enlightenment emerged, challenging traditional authority and promoting reason and individual liberty.
Absolutism
Absolutism emerged in response to the religious and political turmoil of the 16th and 17th centuries. Monarchs sought to consolidate their authority by centralizing power, suppressing dissent, and establishing standing armies. In France, Louis XIV epitomized the absolutist ideal, declaring, “I am the state.”
Enlightenment
The Enlightenment, a philosophical and intellectual movement, emerged in the 17th and 18th centuries. Its proponents, known as philosophes, emphasized the power of human reason, individual rights, and the importance of scientific inquiry. They challenged traditional authority, religious dogma, and the divine right of kings.
Tensions between Absolutism and Enlightenment
The rise of absolutism and the Enlightenment created significant tensions. Monarchs sought to maintain their authority, while Enlightenment thinkers advocated for individual liberty and the limits of royal power. These tensions culminated in revolutions, such as the French Revolution, that challenged the foundations of absolutism and established new political systems based on Enlightenment principles.
User Queries: Ap Euro Period 1 Review
What is the significance of the Renaissance in AP Euro Period 1?
The Renaissance marked a profound cultural and intellectual rebirth in Europe, characterized by a renewed interest in classical learning, humanism, and artistic innovation. It laid the groundwork for the Scientific Revolution and the Enlightenment.
How did the Reformation impact European society?
The Reformation triggered religious conflicts and political upheaval, leading to the division of Western Christianity and the rise of Protestantism. It also challenged the authority of the Catholic Church and contributed to the development of modern nation-states.
What were the motivations behind European exploration during Period 1?
European explorers were driven by a combination of economic, political, and religious motives. They sought new trade routes to Asia, expanded their empires, and spread Christianity to the Americas, Africa, and Asia.