Gizmos distance time graphs answers offer a comprehensive exploration into the realm of motion, providing a powerful tool for visualizing and analyzing the relationship between distance and time. These graphs serve as indispensable resources in various fields, enabling scientists, engineers, and students alike to gain invaluable insights into the dynamics of moving objects.
Understanding distance and time data is crucial for constructing accurate and informative graphs. Distance refers to the length of the path traveled by an object, while time represents the duration of the motion. By plotting distance and time data on a graph, we can visualize the object’s motion and extract meaningful information.
Gizmos Distance Time Graphs
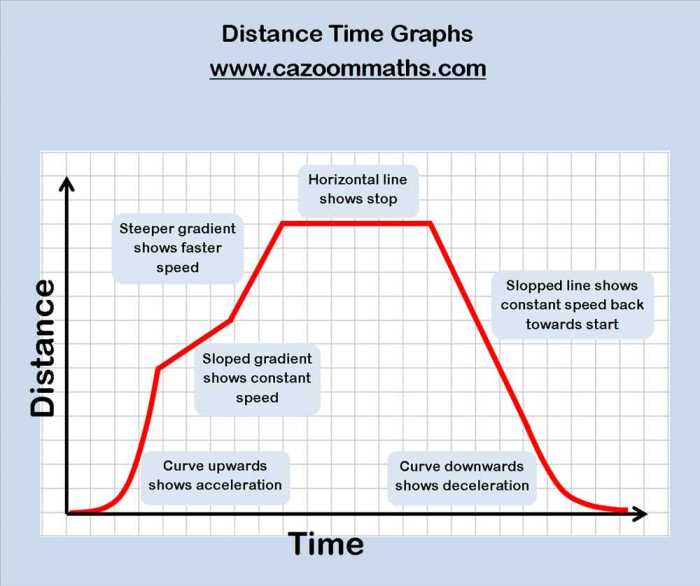
Gizmos distance time graphs are visual representations of the relationship between the distance traveled by an object and the time it takes to travel that distance.
These graphs are used to analyze the motion of objects and to determine their velocity and acceleration.
Purpose and Uses
Gizmos distance time graphs are used for a variety of purposes, including:
- Determining the velocity of an object
- Determining the acceleration of an object
- Analyzing the motion of objects
- Predicting the future motion of objects
Understanding Distance and Time Data
Distance and time are fundamental concepts in physics and are closely related in the study of motion. Distance refers to the length or displacement of an object from a reference point, while time measures the duration of an event or process.
Plotting Distance and Time Data on a Graph
Graphs are a powerful tool for visualizing the relationship between distance and time. To plot distance and time data on a graph, follow these steps:
- Label the x-axis as “Time” and the y-axis as “Distance.”
- Choose an appropriate scale for both axes.
- Plot the data points on the graph by marking the time on the x-axis and the corresponding distance on the y-axis.
- Connect the data points with a line or curve to represent the motion of the object.
By plotting distance and time data on a graph, we can visually analyze the object’s motion and determine its speed, acceleration, and other important characteristics.
Types of Distance Time Graphs
Distance time graphs are graphical representations of the relationship between the distance traveled by an object and the time taken to cover that distance. Different types of distance time graphs represent different types of motion. The two main types of distance time graphs are linear and nonlinear.
Linear Distance Time Graphs
Linear distance time graphs are straight lines. They represent objects moving with constant speed. The slope of the graph represents the speed of the object. The steeper the slope, the faster the object is moving. Linear distance time graphs can be used to calculate the distance traveled by an object in a given time or the time taken to cover a given distance.
Nonlinear Distance Time Graphs
Nonlinear distance time graphs are not straight lines. They represent objects moving with non-constant speed. The shape of the graph depends on the type of motion. For example, a parabolic graph represents an object moving with constant acceleration. A sinusoidal graph represents an object moving with simple harmonic motion.
Interpreting Distance Time Graphs
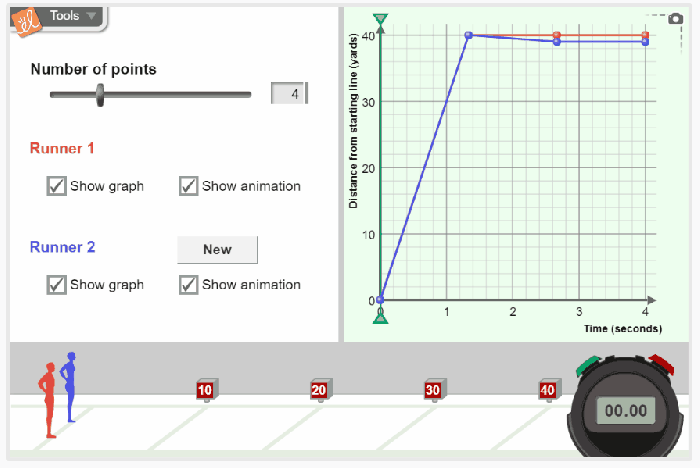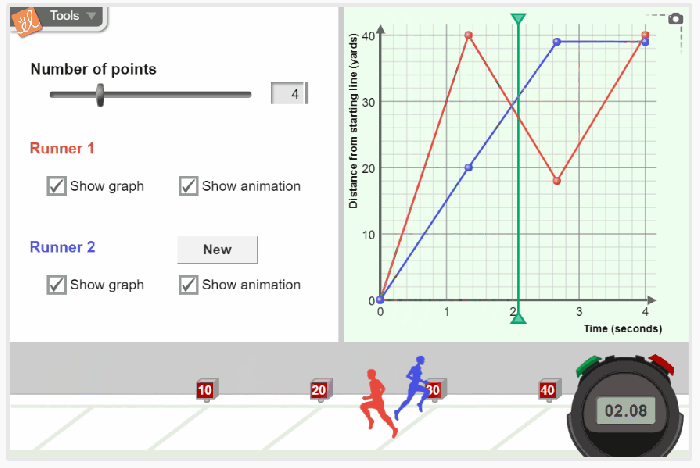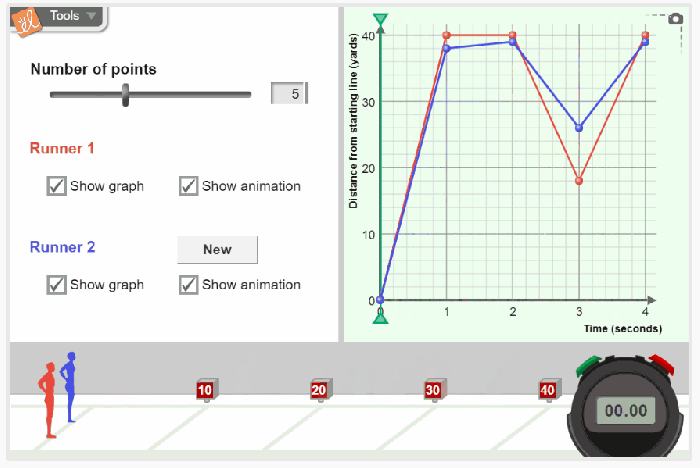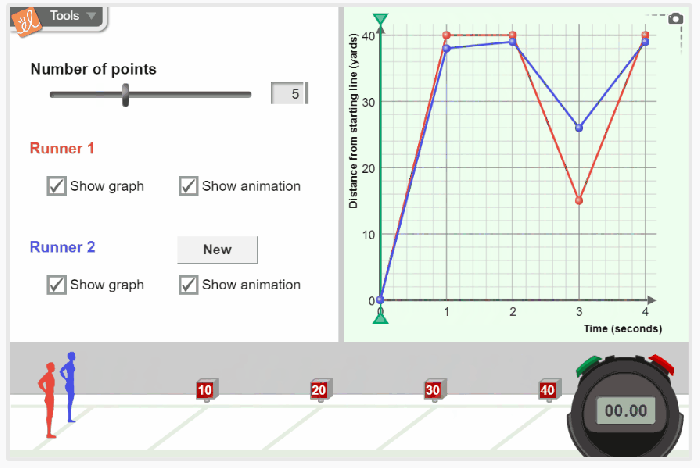
Distance-time graphs are a graphical representation of the relationship between the distance traveled by an object and the time taken to travel that distance. They are useful for visualizing and analyzing the motion of an object.
The slope of a distance-time graph represents the rate of change of distance with respect to time, which is known as the speed or velocity of the object. A positive slope indicates that the object is moving in the positive direction (increasing distance), while a negative slope indicates that the object is moving in the negative direction (decreasing distance).
Total Distance Traveled
The total distance traveled by an object can be determined by finding the area under the distance-time graph. This area can be calculated using the formula:
“`Total distance = (1/2)
- (base)
- (height)
“`where:* base = time interval
height = average speed
Time Taken for a Specific Distance
The time taken for an object to travel a specific distance can be determined by finding the x-intercept of the distance-time graph. The x-intercept represents the time at which the object has traveled the specified distance.
Applications of Distance Time Graphs
Distance time graphs are powerful tools that find applications in various fields, providing valuable insights into the motion of objects.
In the field of physics, distance time graphs are used to analyze and visualize the motion of objects. They help determine the velocity, acceleration, and displacement of objects, aiding in understanding the principles of kinematics.
Engineering
In engineering, distance time graphs are employed in the design and optimization of transportation systems. They assist in planning routes, estimating travel times, and evaluating the performance of vehicles.
Sports Science
Sports scienceutilizes distance time graphs to analyze the performance of athletes. They help coaches and trainers assess speed, endurance, and acceleration, enabling them to develop effective training strategies.
Urban Planning
In urban planning, distance time graphs contribute to the design of efficient transportation networks. They aid in understanding traffic patterns, optimizing traffic flow, and reducing congestion.
Wildlife Biology
Wildlife biologyemploys distance time graphs to study the movement patterns of animals. They help researchers track the migration, foraging behavior, and habitat use of various species.
While distance time graphs offer valuable insights, they also have limitations. They assume constant velocity or acceleration, which may not always be the case in real-world scenarios.
Tips for Creating Effective Distance Time Graphs: Gizmos Distance Time Graphs Answers

Creating clear and informative distance time graphs is essential for effective data visualization. Here are some guidelines to help you create graphs that are both visually appealing and easy to interpret:
Choosing appropriate scales:The scales on the x and y axes should be chosen carefully to ensure that the data is presented in a way that is both accurate and easy to read. The x-axis should typically represent time, while the y-axis represents distance.
Labeling axes:The axes of the graph should be clearly labeled with the appropriate units of measurement. This will help readers to understand what the data represents and how it is being measured.
Using color or symbols:Color or symbols can be used to differentiate between different data sets or to highlight specific features of the graph. For example, you could use different colors to represent different objects or use symbols to represent different types of events.
Choosing Appropriate Scales
- The scales on the x and y axes should be chosen carefully to ensure that the data is presented in a way that is both accurate and easy to read.
- The x-axis should typically represent time, while the y-axis represents distance.
- The scales should be chosen so that the data points are evenly distributed across the graph.
- The scales should also be chosen so that the graph is easy to read and interpret.
Labeling Axes
- The axes of the graph should be clearly labeled with the appropriate units of measurement.
- This will help readers to understand what the data represents and how it is being measured.
- The labels should be placed on the axes in a way that is easy to read and understand.
Using Color or Symbols, Gizmos distance time graphs answers
- Color or symbols can be used to differentiate between different data sets or to highlight specific features of the graph.
- For example, you could use different colors to represent different objects or use symbols to represent different types of events.
- When using color or symbols, it is important to choose colors and symbols that are easy to distinguish from each other.
- You should also use color or symbols consistently throughout the graph so that readers can easily identify the different data sets or features.
Resources for Distance Time Graphs
Distance time graphs are valuable tools for visualizing and analyzing motion. Numerous resources are available to enhance your understanding of these graphs.
Online Resources
Interactive Simulations
PhET
Distance vs. Time Graphs (https://phet.colorado.edu/sims/html/distance-time-graphs/latest/distance-time-graphs_en.html)
Gizmos
Distance Time Graphs (https://www.explorelearning.com/science/simulations/distance-time-graphs/)
Textbooks
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics, 10th Edition by Serway and Jewett
College Physics, 11th Edition by Young and Freedman
Software
Logger Pro by Vernier
MotionGraph by Motion Engineering, Inc.
Query Resolution
What are the different types of distance time graphs?
There are various types of distance time graphs, including linear graphs (indicating constant speed), nonlinear graphs (indicating changing speed), and parabolic graphs (indicating accelerated motion).
How can I determine the speed of an object using a distance time graph?
The speed of an object can be determined by calculating the slope of the distance time graph. The slope represents the rate of change of distance with respect to time, which is equivalent to speed.
What are the applications of distance time graphs in real-world scenarios?
Distance time graphs find applications in numerous fields, including transportation planning, sports analysis, and engineering. They are used to optimize travel routes, analyze athlete performance, and design efficient mechanical systems.